Windows Network Technologies
Shared resources
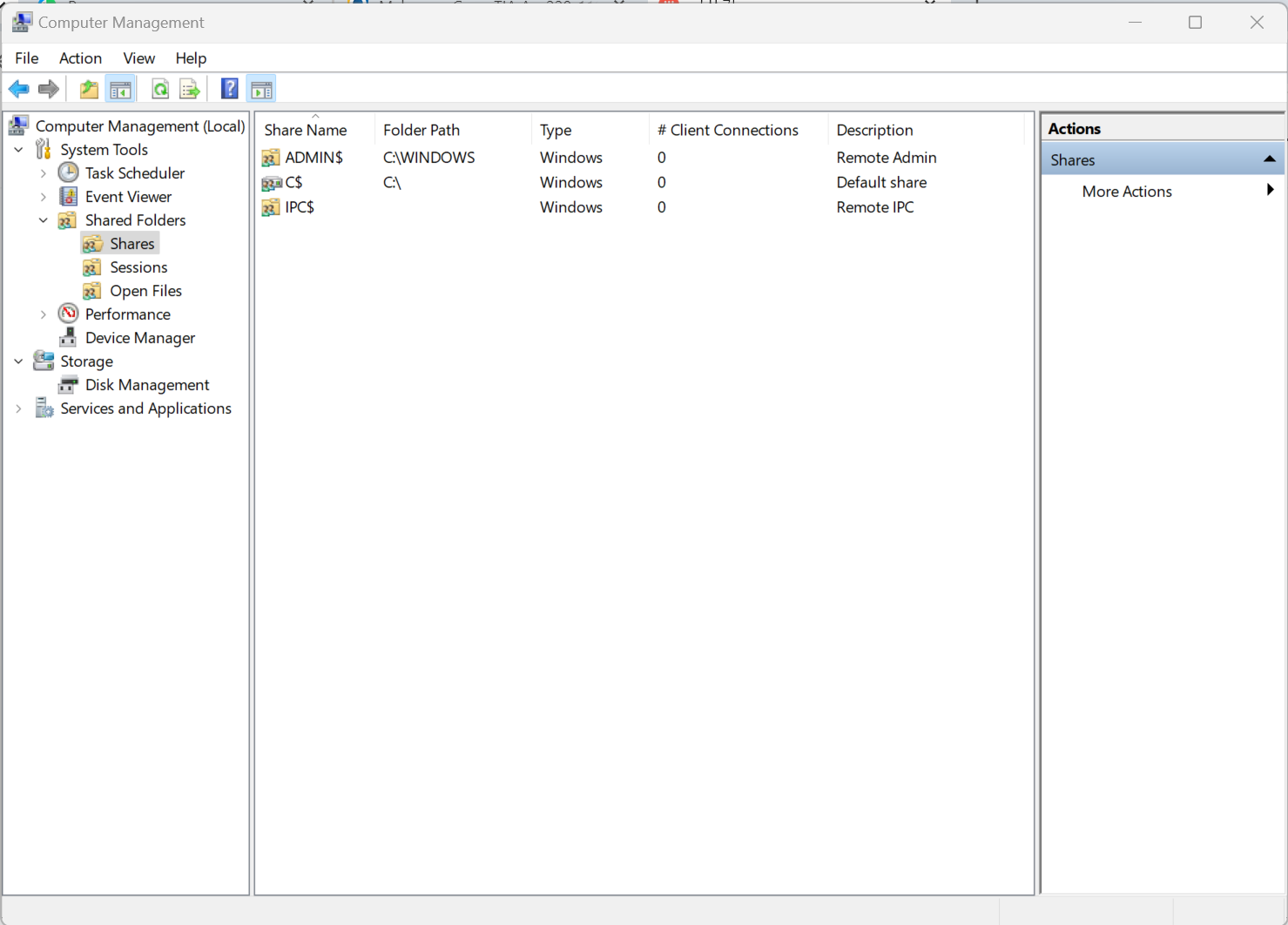
- Make a folder or printer available on the network - "Share" with others, view in File Explorer
- Assign (map) a drive letter to a share - Access a file server, Reconnect automtically
- Shares ending with a dollar sign ($) are "hidden" - Not a security feature
- Administrative Tools / Computer Management
Mapping drives
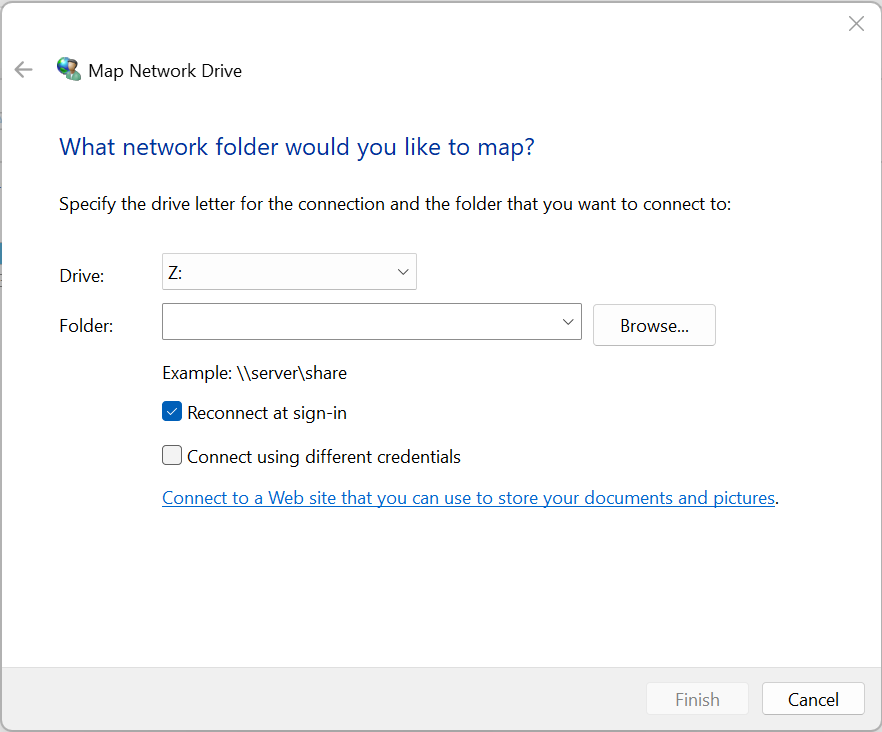
- Access a share - This PC / Map network drive
- Local drive letter and share name - may require additional authentication
- Or use the command line - net use <drive letter> "\\<servername>\<sharename>"
Sharing Printers
- Similar to sharing a folder - But it's a printer instead
- Printer Properties - Access through File Explorer, the settings app, or any other Printer Properties, Sharing an existing printer
Proxy settings
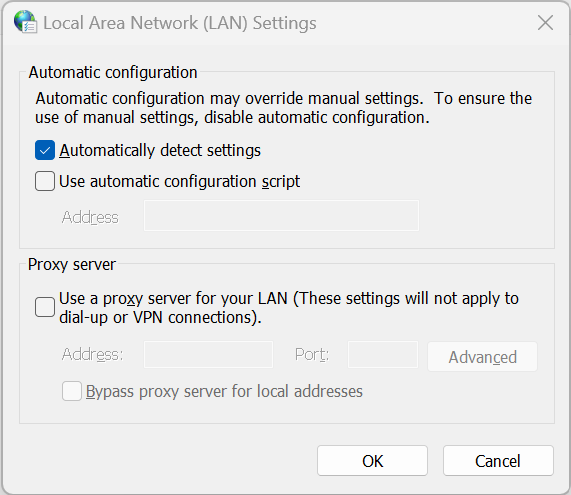
- Change the traffic flow - An Internet go-between
- Settings > Network and Internet - Or use Control Panel > Internet Options > Connections > LAN settings
- Define address and exceptions - Proxies don't work for everything
Network locations
- Private - Share and connect to devices, home or work network
- Public - No sharing or connectivity, Public Wi-Fi
- Customize security settings - Profile is determined automatically, Cahnge the setting at anytime
Network Paths
- View network paths in File Explorer - Server and Share name
- Map network drive - Add a drive letter
- Disconnect - Toolbar, Right click the drive
Metered connections
- Reduce data usage - Slow network links, Liminited bandwidth, Usage-based blilng
- Can modify application communication - Windows updates, Onedrive sync
Configuring Windows Firewall
Windows Defender Firewall
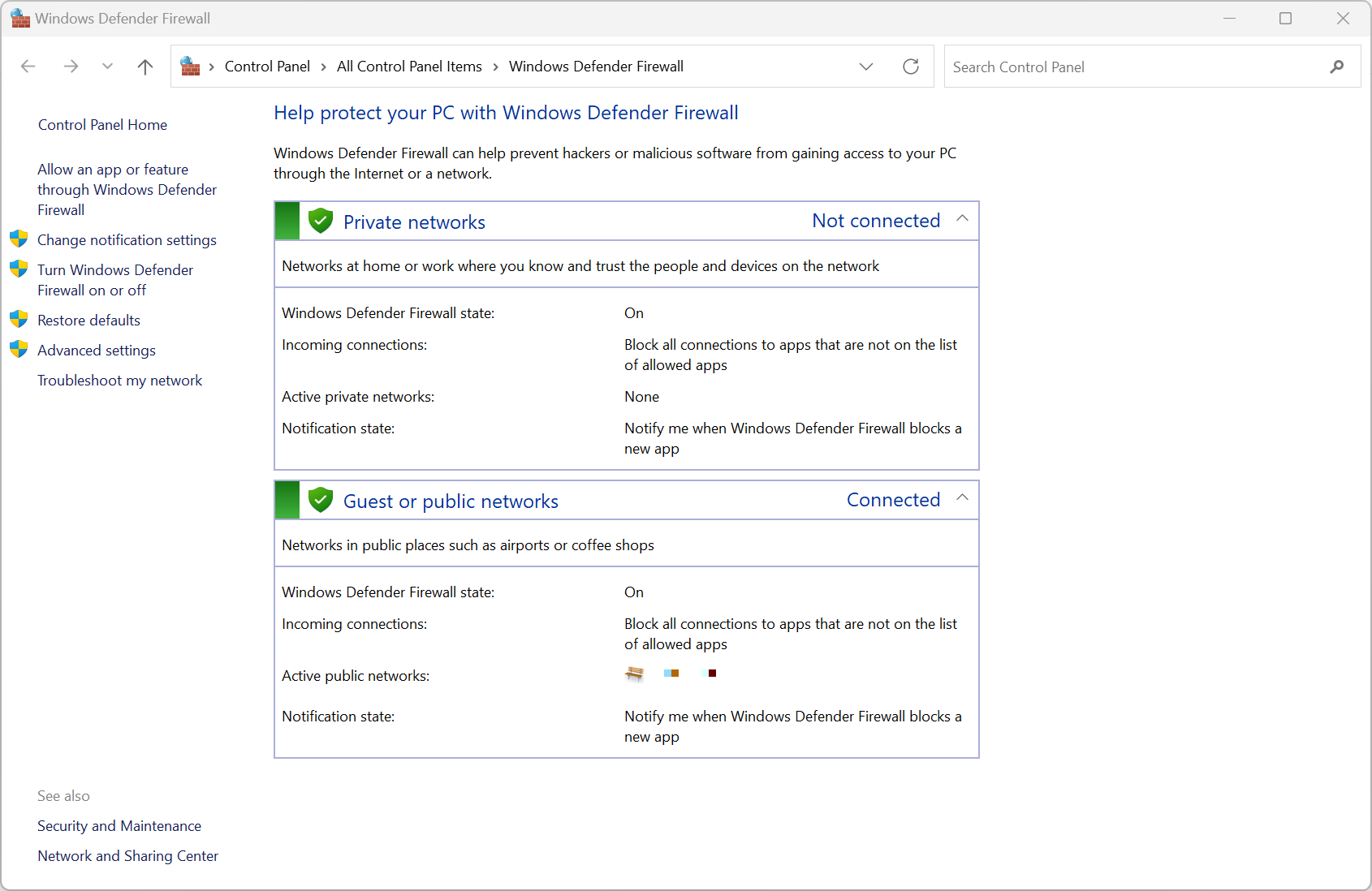
- Your firewall should always be enabled - Sometimes you need to troubleshoot
- Temporarily disable from the main screen - Turn Windows Firewall on or off, Requires eveluated permission
- Different settings for each network type - Public / Private
- -> Different networks having different security concerns
Windows Firewall configuration
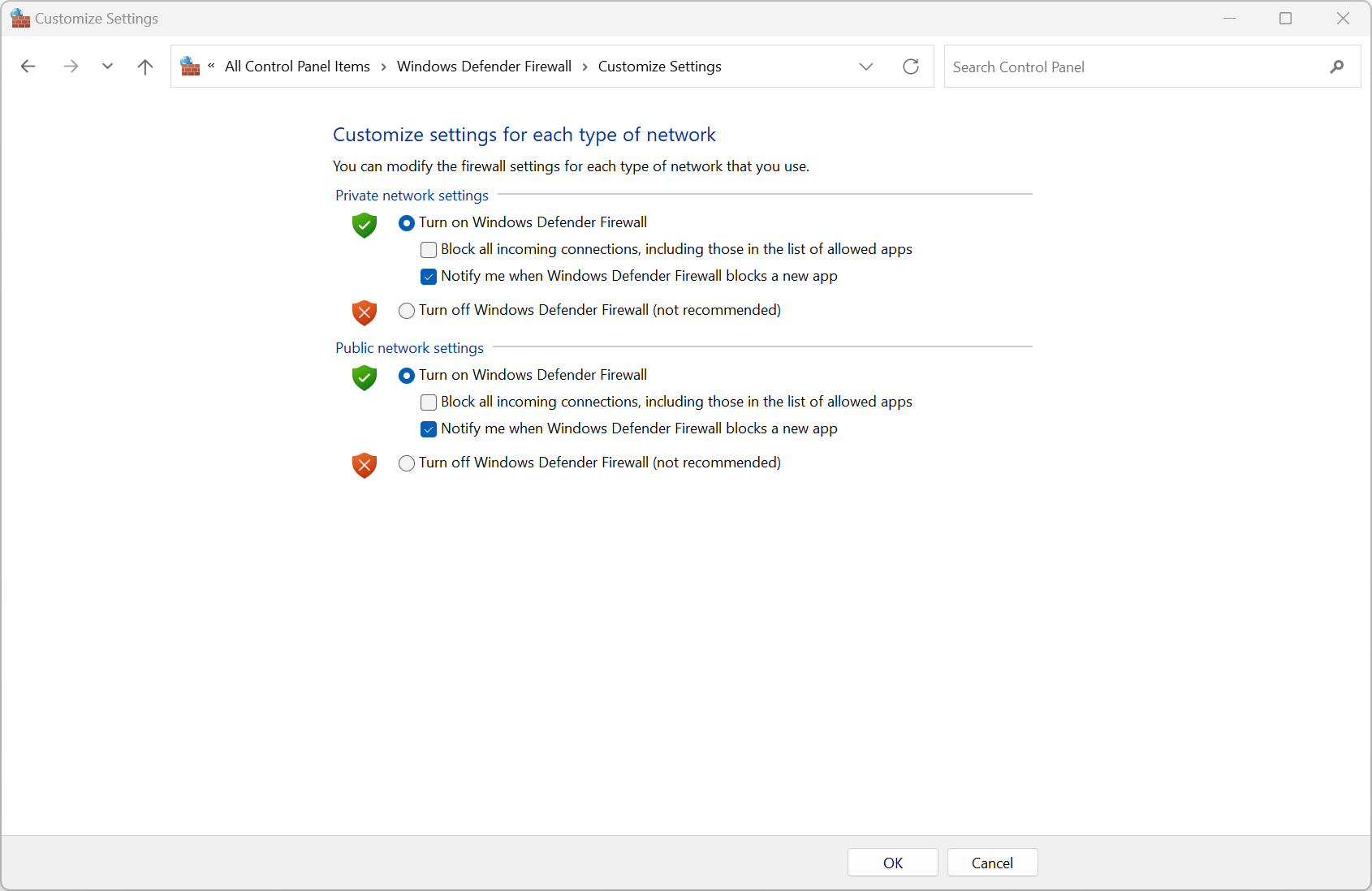
- Block all incoming connections - Ignore your exception list, Useful when you need the most security
- Modify notification - App blocking
Creating a firewall exception
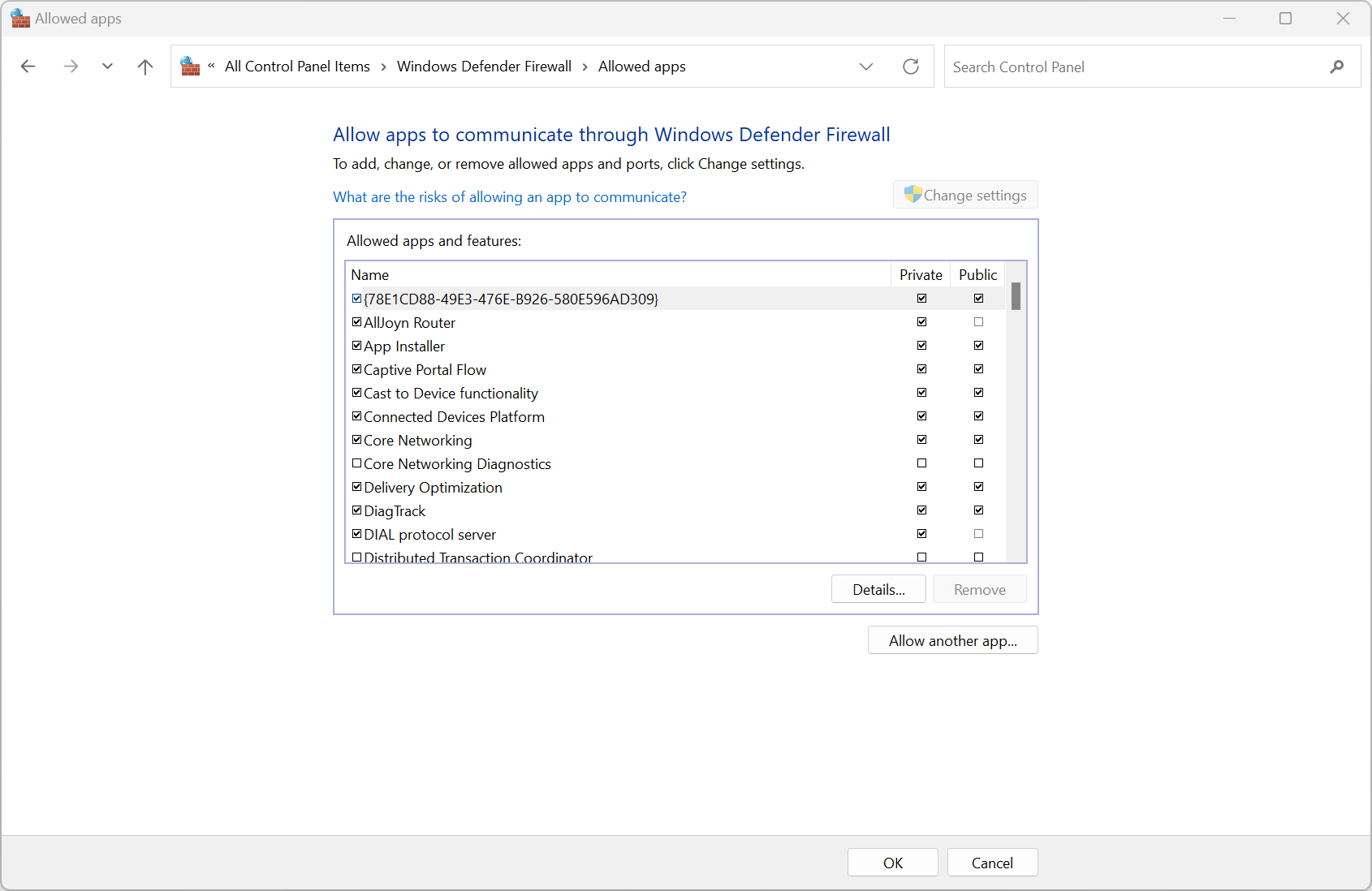
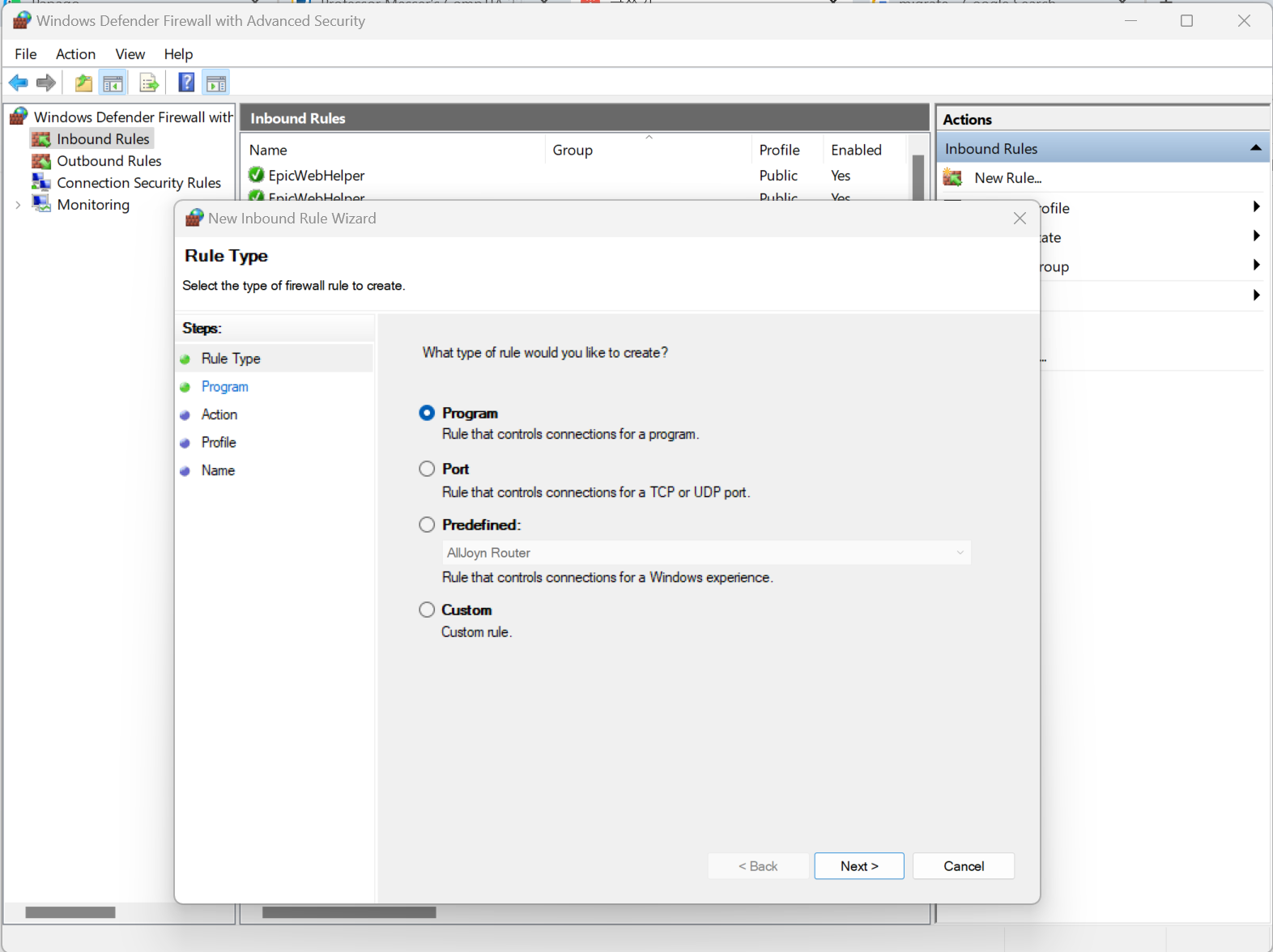
- Allow an app or feature through Windows Firewall - The more secure exception
- Port number - Block or allow
- Predefined exceptions - List of common exceptions
- Custom rule - Every firewall option
=> Go to 'Advanced Security' > right click 'Inbound/Outbound' > 'New rule'
Windows IP Address Configuration
How Windows gets an IP address
- DHCP (Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol)
- Automatic IP addressing
- This is the default
- APIPA (Automatic Private IP Addressing) - if DHCP is not working
- There is no static address or DHCP server
- Communicate locally (link-local address)
- Assigns 169.254.1.0 to 169.254.254.255
- No Internet connectivity
- Static address
- Assign all IP address parameters manually
- You need to know very specific details
TCP/IP host addresses
- IP Address - Unique identifier
- Subnet mask - Identifies the subnet
- Gateway - The route off the subnet to the rest of the world
- -> to provide you the bare minimum of connectivity outside of your network
- DNS (Domain Name Service) - Converts domain names to IP addresses (reverse OK!)
- DHCP (Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol) - Automates the IP address configuration process, Addresses can be dynamic or static
- Loopback address - 127.0.0.1 (It's always there!)
- -> If you want to troubleshoot your system to see if your IP stack is working properly it's very common to ping your loopback
A backup for the DHCP server
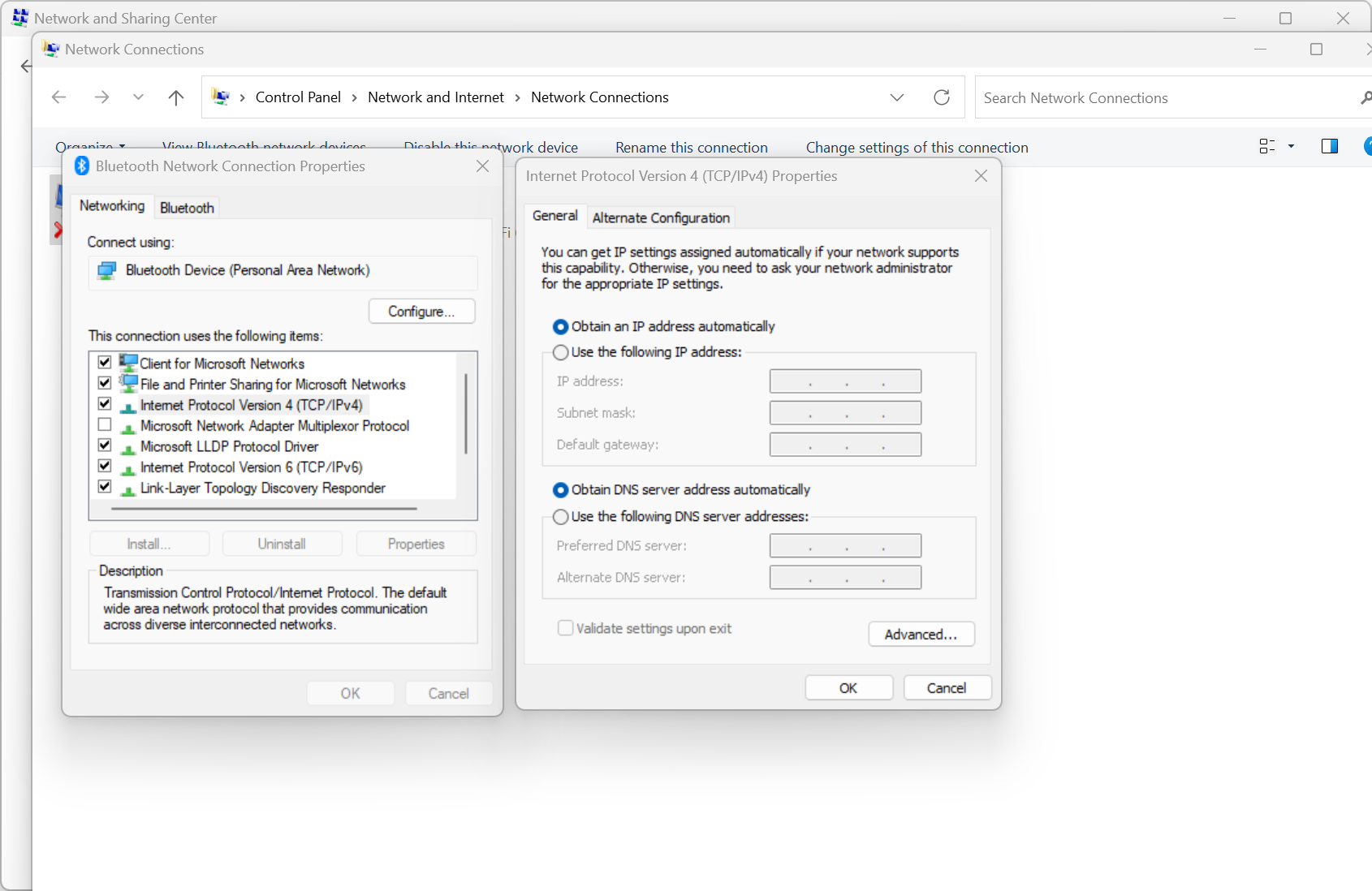
- Multiple DHCP servers should be installed for redundancy - There will always be one available
- If a DHCP server isn't available, Windows uses the Alternate Configuration - The default is APIPA addressing
- You can also configure a static IP address - Keep working normally
=> 'Control Panel' - 'Network and Sharing center' - 'Change adapter settings'
Windows Network Connections
Network Setup
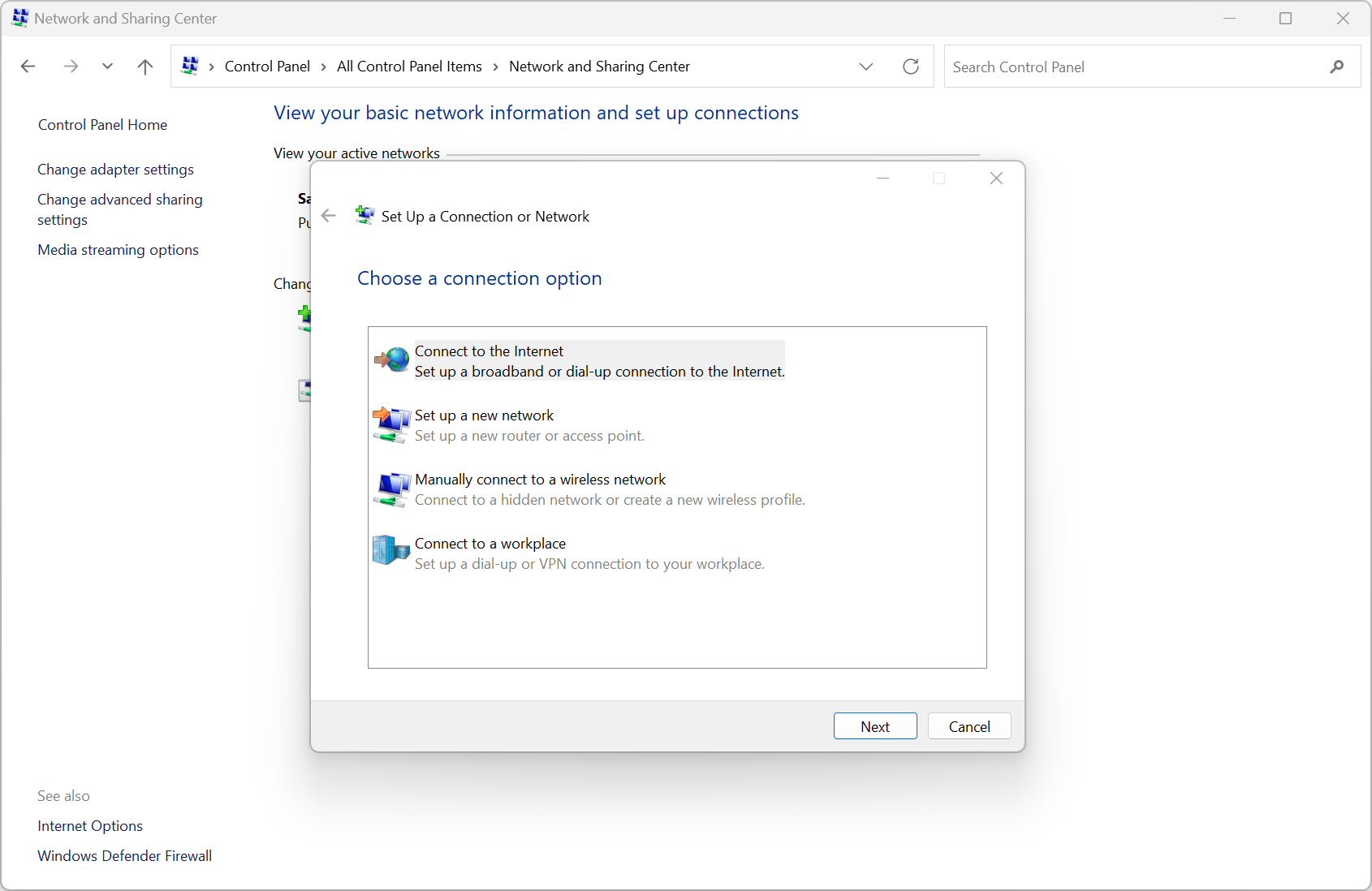
- Control Panel - Netowork and Sharing Center -> Set up a new connection or network
- Step-by-Step wizard - Confirmation during the process
- Many different connections - Direct, VPN, dial-up, etc
- -> 'Set Up a Connection or Network'
VPN concentrators
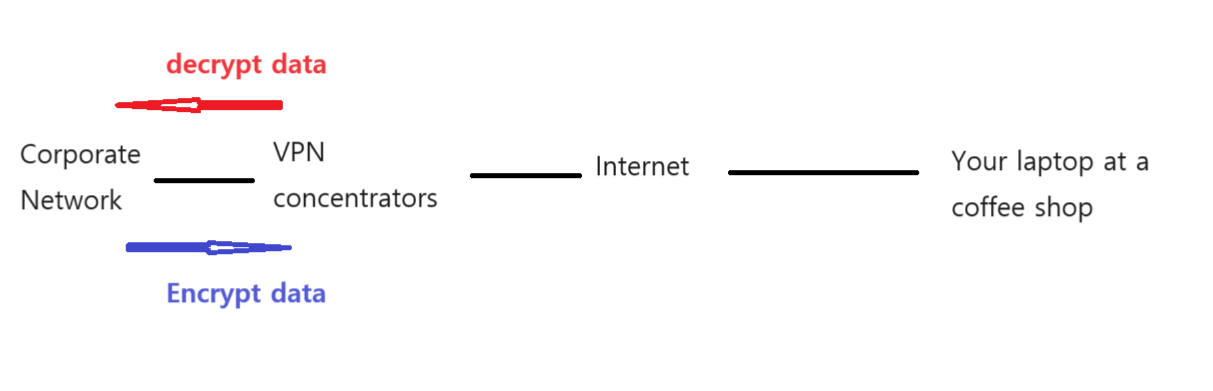
- Built-in VPN Client - Included with Windows, Connect to a workplace (own)
- Integrate a smart card - Multi-factor authentication -> Something you know/have/are
- Connect from the network status icon - Click and provide credentials
Wireless connections
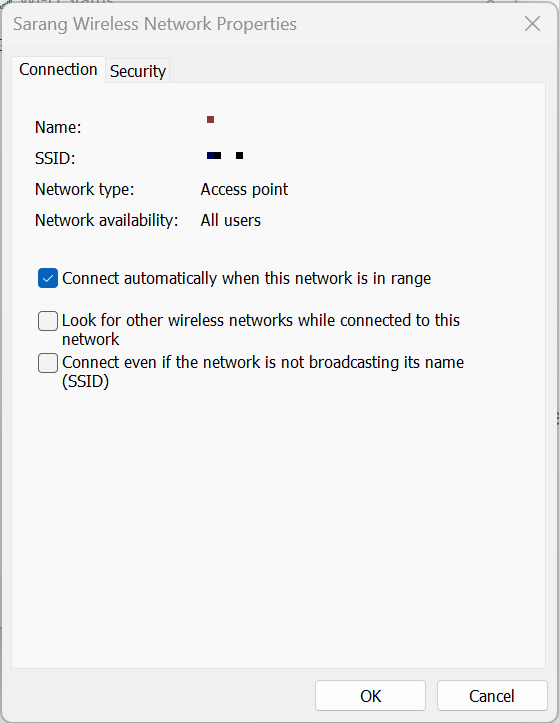
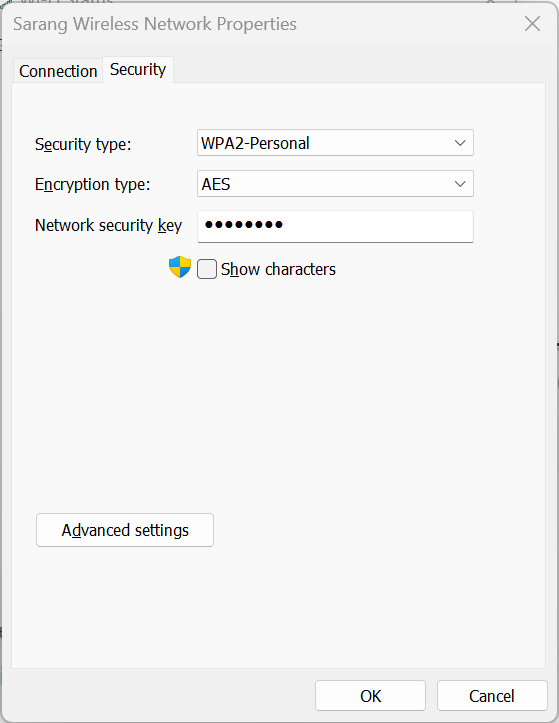
- Network name - SSID (Service Set IDentification)
- Security type - Encryption method (WPA2, WPA2 Enterprise, etc)
- Encryption type - TKIP(Temporary Key Integrity Protocol), AES(Advanced Encryption Standard)
- Security Kep - WPA2 - Personal -> Pre-shared key, WPA2 - Enterprise -> 802.1X authentication
Wired connections
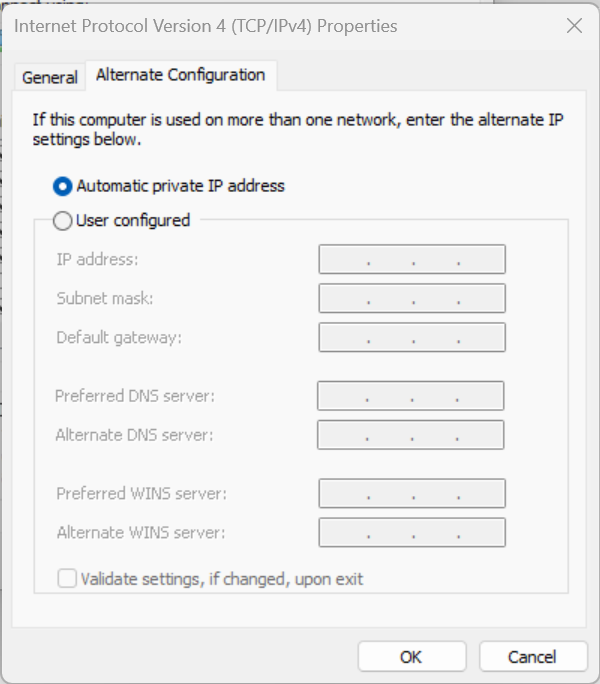
- Ethernet cable - Direct connection (easier connection)
- Fastest connection is the default - Ethernet, Wireless, WWAN(Wireless Wide Area Network)
- Alternative configurations - When DHCP isn't available
WWAN connections
- Wireless Wide Area Network - Built-in mobile technology
- Hardware adapter - Antenna connections (ex: Wi-Fi)
- USB connected or 802.11 wireless - Tether, Hotspot
- Requires third-party software - Each provider is different
- -> would allow you access to the Internet
'CompTIA A+ > 220-1102' 카테고리의 다른 글
| 1.8 Operating System Types (0) | 2024.02.16 |
|---|---|
| 1.7 Installing Applications (0) | 2024.02.16 |
| 1.5 Windows Settings (0) | 2024.02.13 |
| 1.4 The Windows Control Panel (0) | 2024.02.13 |
| 1.3 The Windows OS (0) | 2024.02.12 |



